Use nullability in Kotlin¶
Before you begin¶
This codelab teaches you about nullability and the importance of
nullsafety. Nullability is a concept commonly found in many programming languages. It refers to the ability of variables to have an absence of value. In Kotlin, nullability is intentionally treated to achievenullsafety.
Prerequisites¶
Knowledge of Kotlin programming basics, including variables, accessing methods and properties from a variable and the
println()andmain()functionsFamiliarity with Kotlin conditionals, including
if/elsestatements and Boolean expressions
What you’ll learn¶
What
nullis.The difference between nullable and non-nullable types.
What
nullsafety is, its importance, and how Kotlin achievesnullsafety.How to access methods and properties of nullable variables with the
?.safe call operator and!!non-null assertion operator.How to perform
nullchecks withif/elseconditionals.How to convert a nullable variable to a non-nullable type with
if/elseexpressions.How to provide a default value when a nullable variable is
nullwith theif/elseexpression or the?:Elvis operator.
What you’ll need¶
A web browser with access to Kotlin Playground
Use nullable variables¶
In Kotlin, you can use
nullto indicate that there’s no value associated with a certain variable. Example:fun main() { val favoriteActor = null }
In Kotlin, there’s a distinction between nullable and non-nullable types:
Nullable types are variables that can hold
null.Non-null types are variables that cannot hold
null.
A type is only nullable if you explicitly let it hold
null. As the error message says, theStringdata type is a non-nullable type, so you can’t reassign the variable tonull.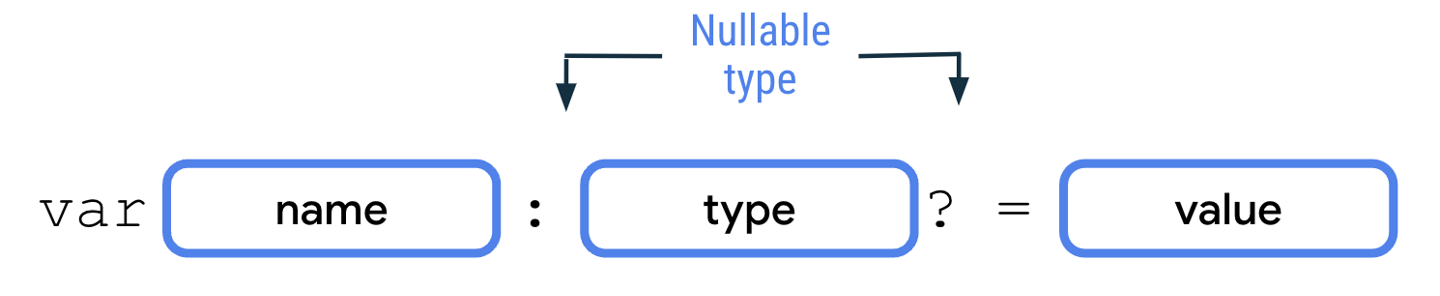
To declare nullable variables in Kotlin, you need to add a
?operator to the end of the type. For example, aString?type can hold either a string ornull, whereas aStringtype can only hold a string. To declare a nullable variable, you need to explicitly add the nullable type. Without the nullable type, the Kotlin compiler infers that it’s a non-nullable type.fun main() { var number: Int? = 10 println(number) number = null println(number) }
Note
While you should use nullable variables for variables that can carry
null, you should use non-nullable variables for variables that can never carrynullbecause the access of nullable variables requires more complex handling. You learn about various techniques to handle nullable variables in the next section.
Handle nullable variables¶
In this section, you learn how to access methods and properties of nullable variables.
The code below produces an error message:
fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = "Sandra Solulu" println(favoriteActor.length) }

This error is a compile error, or compile-time error. A compile error happens when Kotlin isn’t able to compile the code due to a syntax error in your code.
Kotlin intentionally applies syntactic rules so that it can achieve
nullsafety, which refers to a guarantee that no accidental calls are made on potentiallynullvariables. This doesn’t mean that variables can’t benull. It means that if a member of a variable is accessed, the variable can’t benull.This is critical because if there’s an attempt to access a member of a variable that’s
null- known as anullreference - during the running of an app, the app crashes because thenullvariable doesn’t contain any property or method. This type of crash is known as a runtime error in which the error happens after the code has been compiled, and runs.Due to the
nullsafety nature of Kotlin, such runtime errors are prevented because the Kotlin compiler forces anullcheck for nullable types. Anullcheck refers to a process of checking whether a variable could benullbefore it’s accessed and treated as a non-nullable type. If you wish to use a nullable value as its non-nullable type, you need to perform anullcheck explicitly. You’ll learn more about this later.
Use the ?. safe call operator¶
You can use the
?.safe call operator to access methods or properties of nullable variables.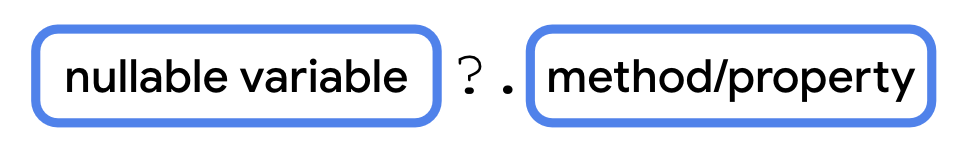
The
?.safe call operator allows safer access to nullable variables because the Kotlin compiler stops any attempt of member access tonullreferences and returnsnullfor the member accessed. Example:fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = "Pigsy Pooh" println(favoriteActor?.length) }
When the below code is run, the output is
null. The program doesn’t crash despite an attempt to access thelengthproperty of anullvariable. The safe call expression simply returnsnull.fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = null println(favoriteActor?.length) }
Note
You can also use the
?.safe call operators on non-nullable variables to access a method or property. While the Kotlin compiler won’t give any error for this, it’s unnecessary because the access of methods or properties for non-nullable variables is always safe.
Use the !! not-null assertion operator¶
You can also use the
!!not-null assertion operator to access methods or properties of nullable variables.
If you use the
!!not-null assertion, it means that you assert that the value of the variable isn’t null, regardless of whether it is or isn’t. You’re telling the compiler, I’m very very very sure that this value isn’t null, don’t complain about it during compile time.Unlike
?.safe-call operators, the use of a!!not-null assertion operator may result in aNullPointerExceptionerror being thrown if the nullable variable is indeednull. Thus, it should be done only when the variable is always non-nullable or proper exception handling is set in place. When not handled, exceptions cause runtime errors. You learn about exception handling later.Example:
fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = "Sandra Solulu" println(favoriteActor!!.length) }
In the above code, if the
!!is removed, the compiler complains:Only safe (?.) or non-null asserted (!!.) calls are allowed on a nullable receiver of type 'kotlin.String?'.
By adding
!!, you’re telling the compiler that the value will never be null, and the compiler won’t complain during compile-time. However, if you were wrong and the value is indeed null, aNullPointerExceptionerror is thrown during run-time.Example of code that will not cause any compile-time error, but will cause a
NullPointerExceptionrun-time error:fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = null println(favoriteActor!!.length) }
Use the if/else conditionals¶
To perform
nullchecks, you can check that the nullable variable isn’t equal tonullwith the!=comparison operator
You can also check if a variable is null using
==An
if/elsestatement can be used together with anullcheck as follows: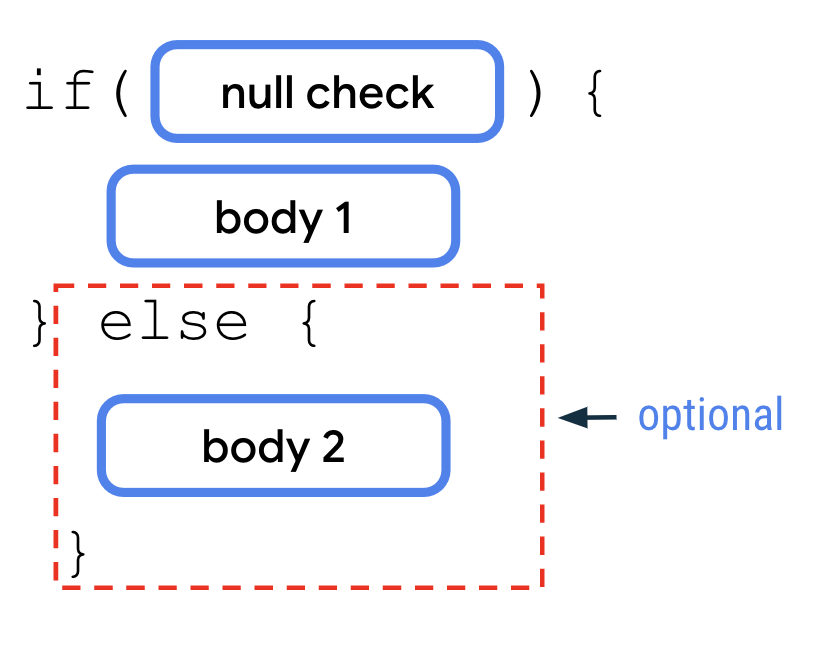
The
nullcheck is more convenient to use with theifcondition when there are multiple lines of code that use the nullable variable. In contrast, the?.safe-call operator is more convenient for a single reference of the nullable variable.Example:
fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = "Sandra Solulu" if (favoriteActor != null) { println("The number of characters in your favorite actor's name is ${favoriteActor.length}.") } else { println("You didn't input a name.") } }
You can also combine the
nullcheck with anif/elseexpression to convert a nullable variable to a non-nullable variable.
Example:
fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = "Sandra Solulu" val lengthOfName = if (favoriteActor != null) { favoriteActor.length } else { 0 } println("The number of characters in your favorite actor's name is $lengthOfName.") }
The
?:Elvis operator is an operator that you can use together with the?.safe-call operator. With the?:Elvis operator, you can add a default value when the?.safe-call operator returnsnull. It’s similar to anif/elseexpression, but in a more idiomatic way.If the variable isn’t
null, the expression before the?:Elvis operator executes. If the variable isnull, the expression after the?:Elvis operator executes.
Example:
fun main() { var favoriteActor: String? = "Sandra Solulu" val lengthOfName = favoriteActor?.length ?: 0 println("The number of characters in your favorite actor's name is $lengthOfName.") }
Conclusion¶
A variable can be set to
nullto indicate that it holds no value.Non-nullable variables cannot be assigned
null.Nullable variables can be assigned
null.To access methods or properties of nullable variables, you need to use
?.safe-call operators or!!not-null assertion operators.You can use
if/elsestatements withnullchecks to access nullable variables in non-nullable contexts.You can convert a nullable variable to a non-nullable type with
if/elseexpressions.You can provide a default value for when a nullable variable is
nullwith theif/elseexpression or the?:Elvis operator.